By Shashikant Nishant Sharma
A systematic literature review is a critical and comprehensive analysis of available research and literature on a specific topic or question. It follows a structured methodology to identify, evaluate, and synthesize all relevant published research on a given subject. This type of review is essential for informing evidence-based decision-making and identifying gaps in current research. In this article, we will delve into the key aspects of conducting a systematic literature review.
The Purpose of a Systematic Literature Review
A systematic literature review stands as a cornerstone in the realm of academic exploration, offering an in-depth and thorough analysis of existing research and literature concerning a specific topic or inquiry. Its methodology is meticulous, employing a structured approach to identify, evaluate, and synthesize all pertinent published research on a given subject. This type of review is instrumental in driving evidence-based decision-making and illuminating the gaps present within current research. In this article, we will unravel the intricacies involved in conducting a systematic literature review.
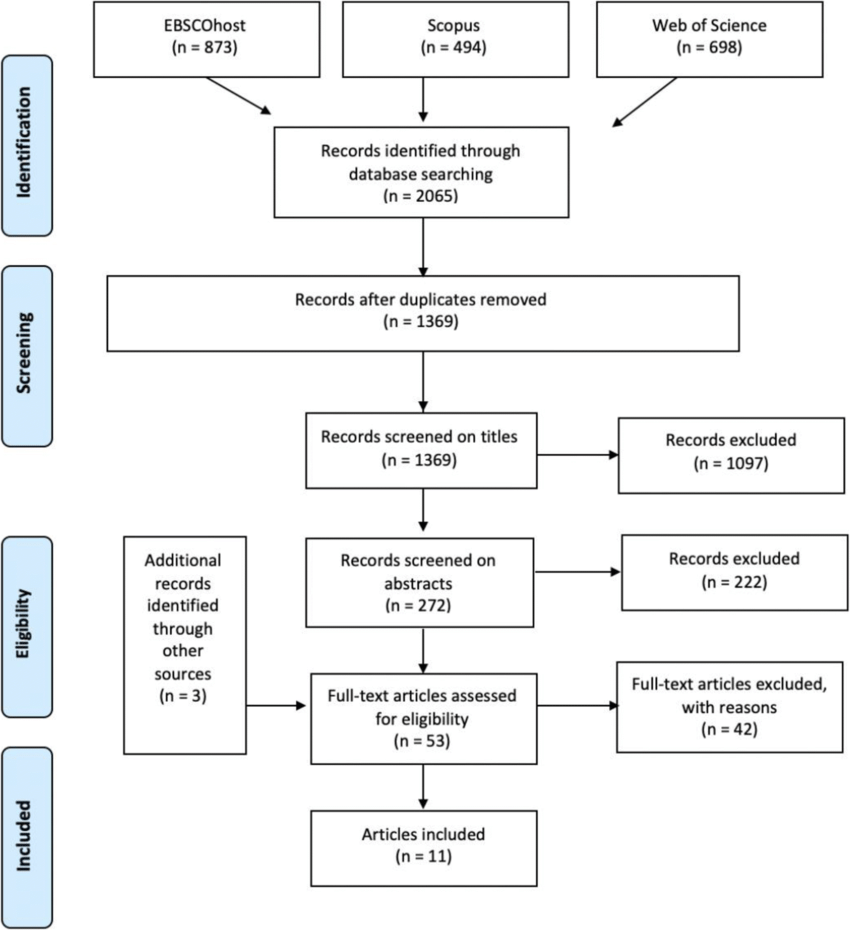
The Purpose of a Systematic Literature Review
The fundamental objective of a systematic literature review is to furnish a robust and unbiased summary of the existing knowledge pertaining to a particular subject. It strives to achieve the following key goals:
- Summarize Existing Research:
- Engage in the aggregation and summarization of findings from prior studies to provide a comprehensive understanding of the topic. Collate and summarize the findings of previous studies to offer an overall understanding of the topic.
- Identify Research Gaps:
- Discern areas where research is deficient or warrants further investigation, acting as a compass for future scholarly endeavors. Pinpoint areas where research is lacking or where further investigation is needed.
- Evaluate Methodologies:
- Critically assess the quality and rigor of methods employed in previous studies, unveiling both strengths and weaknesses. Assess the quality and rigor of the methods used in previous studies to identify strengths and weaknesses.
- Inform Decision-making:
- Serve as a foundational resource for facilitating informed decisions, whether within academia, policy formulation, or practical applications. Provide a foundation for making informed decisions, whether in academia, policy, or practice.
The primary goal of a systematic literature review is to provide a robust and impartial summary of existing knowledge on a particular subject. It aims to:
- Summarize Existing Research:
- Identify Research Gaps:
- Evaluate Methodologies:
- Inform Decision-making:
Key Steps in Conducting a Systematic Literature Review
- Formulating the Research Question or Objective:
- Clearly define the research question or objective that the review aims to address. This ensures focus and clarity throughout the process. Begin by articulating a clear and precise research question or objective that the review aims to address. This sets the stage for maintaining focus and clarity throughout the review process.
- Developing Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria:
- Establish specific criteria for including or excluding studies based on parameters such as publication date, study design, population, or outcomes of interest. Establish specific criteria for study inclusion or exclusion based on parameters such as publication date, study design, target population, or outcomes of interest.
- Systematic Search and Selection of Studies:
- Conduct a thorough and systematic search across relevant databases and sources to identify all pertinent studies. The search process should be transparent, replicable, and documented in detail.
- Apply the inclusion and exclusion criteria to select studies that meet the predefined criteria.
- Initiate a comprehensive and systematic search across pertinent databases and sources to identify all relevant studies. The search process should be transparent, replicable, and meticulously documented.
- Apply the predefined inclusion and exclusion criteria to meticulously select studies that align with the set criteria.
- Data Extraction and Analysis:
- Extract relevant data from the selected studies using a standardized data extraction form. This could include study characteristics, methodologies, key findings, and other relevant information.
- Extract pertinent data from the selected studies using a standardized data extraction form. This may encompass study characteristics, methodologies, key findings, and other pertinent details.
- Analyze and synthesize the extracted data to unveil patterns, trends, and recurring themes.
- Quality Assessment:
- Evaluate the quality and rigor of the selected studies, considering factors such as study design, sample size, methodology, and potential biases. Conduct a rigorous evaluation of the quality and rigor of the selected studies, considering critical factors such as study design, sample size, methodology, and potential biases.
- Synthesis and Presentation of Results:
- Synthesize the findings from the selected studies, organizing them in a coherent and structured manner.
- Present the results using appropriate formats, such as tables, graphs, or narrative summaries.
- Interpretation and Conclusion:
- Interpret the synthesized findings and draw conclusions based on the collective evidence.
- Discuss implications, limitations, and potential future research directions.
Advantages of a Systematic Literature Review
- Comprehensive Understanding: Provides a comprehensive and organized overview of existing knowledge on a topic.
- Reduction of Bias: Minimizes bias by following a structured and systematic approach to study selection and analysis.
- Evidence-based Decision-making: Informs decision-making in various domains, including healthcare, policy, education, and more.
- Identifying Research Gaps: Highlights gaps in current research, guiding future research initiatives.
Challenges and Limitations
- Publication Bias: The inclusion of only published studies can introduce publication bias, as negative or inconclusive results may not be published.
- Resource Intensiveness: Conducting a systematic literature review requires significant time, resources, and expertise.
- Incomplete or Inaccessible Data: Some relevant studies may not be accessible or may lack detailed information.
Conclusion
A systematic literature review is a valuable tool for synthesizing existing knowledge and informing decision-making across various fields. By following a structured methodology, it provides a rigorous and objective analysis of the available research, aiding in the advancement of knowledge and the identification of research gaps. Researchers, policymakers, and practitioners can use the insights gained from systematic literature reviews to make informed decisions and contribute to the progression of their respective domains. A systematic literature review stands as a valuable and indispensable tool for synthesizing existing knowledge and informing decision-making across a plethora of academic and practical domains. Its structured methodology facilitates a rigorous and unbiased analysis of available research, propelling the advancement of knowledge and shedding light on critical research gaps. Researchers, policymakers, and practitioners can leverage the insights garnered from systematic literature reviews to make informed decisions and contribute meaningfully to the progression of their respective fields of study.
References
Dehalwar, K., & Sharma, S. N. (2023). Fundamentals of Research Writing and Uses of Research Methodologies. Edupedia Publications Pvt Ltd.
Dziopa, F., & Ahern, K. (2011). A systematic literature review of the applications of Q-technique and its methodology. Methodology.
Kitchenham, Barbara, et al. “Systematic literature reviews in software engineering–a systematic literature review.” Information and software technology 51.1 (2009): 7-15.
Rother, E. T. (2007). Systematic literature review X narrative review. Acta paulista de enfermagem, 20, v-vi.
Sharma, S.N., ed. New perspectives in sociology and allied fields. EduPedia Publications (P) Ltd, 2016.
Sharma, S.N. (2023). “Understanding Citations: A Crucial Element of Academic Writing.” Track2Training
Xiao, Y., & Watson, M. (2019). Guidance on conducting a systematic literature review. Journal of planning education and research, 39(1), 93-112.

You must be logged in to post a comment.