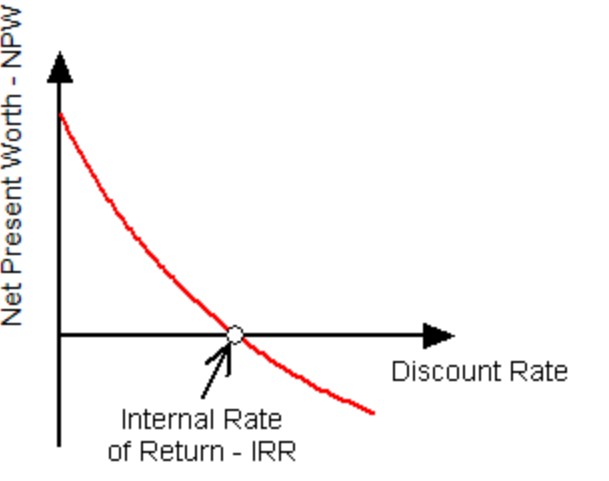
1️⃣ What is Internal Rate of Return (IRR)?
Internal Rate of Return (IRR) is the discount rate at which the Net Present Value (NPV) of a project becomes zero.
In simple terms:
IRR is the rate of return a project is expected to generate over its life.
It considers:
- Time value of money
- Multiple cash inflows and outflows
- Long-term project performance
IRR is widely used in:
- Real estate development
- Infrastructure planning
- PPP projects
- Urban redevelopment
- Sustainable building investments
2️⃣ IRR Formula
IRR is calculated using the NPV equation.
🔹 NPV Formula
NPV=−Initial Investment+∑(1+r)tCash Flowt
Where:
- r = discount rate
- t = time period
- IRR is the value of r when:
NPV=0
So,0=−Initial Investment+∑(1+IRR)tCash Flowt
Since the equation cannot be solved directly, IRR is found using:
- Trial and error
- Interpolation method
- Financial calculator
- Excel IRR function
3️⃣ Why IRR is Important in Architecture & Planning
IRR helps planners and architects:
- Compare multiple development proposals
- Evaluate long-term infrastructure investments
- Justify PPP concession models
- Assess sustainable building investments
- Decide between design alternatives
- Determine project viability
If:
- IRR > Required Rate of Return (Cost of Capital) → Project is acceptable
- IRR < Required Rate of Return → Project should be rejected
4️⃣ Step-by-Step IRR Calculation with Example
✅ Example 1: Small Commercial Building Project
Initial Investment (Year 0)
₹1,00,000
Expected Cash Inflows:
Year 1 = ₹60,000
Year 2 = ₹60,000
Step 1: Try 10% Discount Rate
NPV=−1,00,000+1.1060,000+1.10260,000 =−1,00,000+54,545+49,587 =+4,132
NPV is positive → IRR is higher than 10%
Step 2: Try 15%
NPV=−1,00,000+1.1560,000+1.15260,000 =−1,00,000+52,174+45,369 =−2,457
NPV is negative → IRR is between 10% and 15%
Step 3: Interpolation Formula
IRR=r1+NPV1−NPV2NPV1×(r2−r1)
Where:
- r1=10%
- r2=15%
- NPV1=4,132
- NPV2=−2,457
IRR=10+4132+24574132×5 IRR≈13.1%
✅ Example 2: Urban Parking Project
Initial Investment = ₹2,50,00,000
Annual Net Cash Flow = ₹40,00,000
Project Life = 8 years
Using financial approximation:
IRR ≈ 14–16%
If the required return is 12%, the project is financially viable.
✅ Example 3: Solar Panel Investment in Office Building
Installation Cost = ₹5,00,000
Annual Savings = ₹1,20,000
Life = 5 years
Using trial method or Excel:
IRR ≈ 18–20%
This supports sustainable investment decision-making.
5️⃣ Applications of IRR in Architecture & Urban Planning
🔹 1. Real Estate Feasibility Studies
- Apartment development
- Commercial complex
- Mixed-use buildings
Helps developers decide project scale and phasing.
🔹 2. Transit-Oriented Development (TOD)
IRR helps evaluate:
- Increased land value
- Higher rental income near transit
- Mixed-use density benefits
🔹 3. Public-Private Partnership (PPP)
IRR determines:
- Concession period
- Revenue sharing ratio
- Private investor attractiveness
🔹 4. Infrastructure Projects
Used for:
- Metro stations
- Bus terminals
- Multi-level parking
- Smart city infrastructure
🔹 5. Sustainable Building Investments
IRR justifies:
- Green roof systems
- Solar panels
- Energy-efficient façade
- Water recycling systems
6️⃣ Advantages of IRR
✔ Considers time value of money
✔ Useful for long-term projects
✔ Easy comparison between alternatives
✔ Widely accepted in financial markets
✔ Useful for PPP and infrastructure projects
7️⃣ Limitations of IRR
❌ Complex to calculate manually
❌ May give multiple IRRs in unusual cash flow patterns
❌ Does not show absolute profit amount
❌ Can mislead if project sizes differ
Therefore, IRR should be used along with:
- NPV
- ROI
- Payback Period
- Cost-Benefit Analysis
8️⃣ Difference Between ROI and IRR
| ROI | IRR |
|---|---|
| Simple profitability ratio | Time-adjusted return |
| Ignores time value | Considers time value |
| Easy to calculate | Requires iteration |
| Short-term focus | Long-term focus |
9️⃣ Practical Use in DPR Preparation
When preparing a Detailed Project Report:
- Estimate yearly cash flows
- Apply discounting
- Calculate IRR
- Compare with cost of capital
- Recommend project acceptance or rejection
🔟 Conclusion
Internal Rate of Return (IRR) is one of the most powerful financial tools in architecture and urban planning. It helps evaluate:
- Real estate viability
- Infrastructure feasibility
- TOD development returns
- Sustainable design investments
- PPP financial attractiveness
For architects and planners, understanding IRR ensures that projects are not only technically sound and aesthetically strong but also financially sustainable.
