1️⃣ What is Net Present Value (NPV)?
Net Present Value (NPV) is a financial evaluation method used to determine the profitability of a project by considering the time value of money.
It answers:
“What is the present value of future cash flows after deducting the initial investment?”
Unlike ROI, NPV accounts for the fact that ₹1 today is worth more than ₹1 in the future.
2️⃣ Concept of Time Value of Money
Money received in the future must be discounted because:
- Inflation reduces purchasing power
- Money has opportunity cost
- There is risk involved
Therefore, future cash flows are converted to present value.
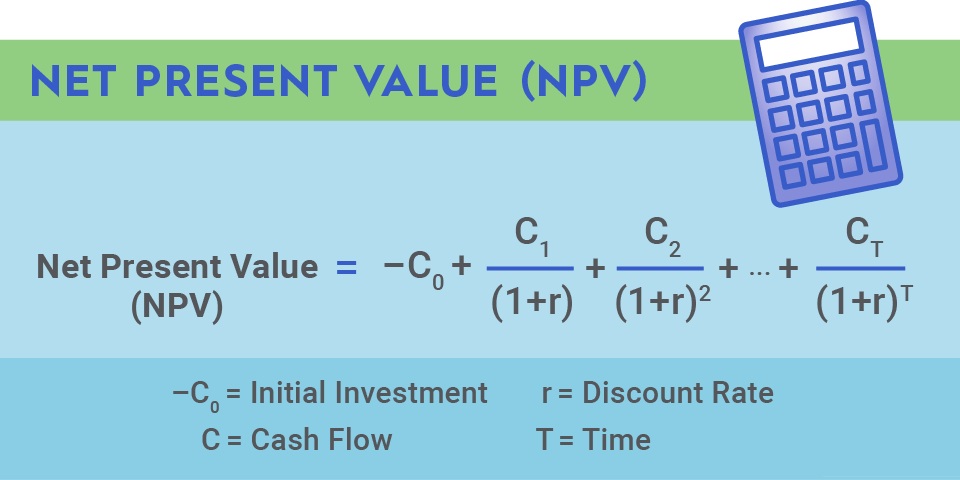
3️⃣ NPV Formula
NPV=−C0+∑(1+r)tCt
Where:
- C0 = Initial investment
- Ct = Cash inflow in year t
- r = Discount rate
- t = Time period
4️⃣ Decision Rule
- If NPV > 0 → Accept the project
- If NPV < 0 → Reject the project
- If NPV = 0 → Break-even
5️⃣ Importance of NPV in Architecture & Planning
NPV is widely used in:
- Real estate feasibility studies
- Urban infrastructure projects
- Metro and transport projects
- Sustainable building investments
- PPP projects
- Smart city development
It helps planners evaluate long-term economic viability.
6️⃣ Step-by-Step Numerical Example
✅ Example 1: Commercial Building Project
Initial Investment (Year 0)
₹1,00,000
Expected Cash Inflows:
Year 1 = ₹60,000
Year 2 = ₹60,000
Discount Rate = 10%
Step 1: Discount Year 1 Cash Flow
PV1=1.1060,000 PV1=54,545
Step 2: Discount Year 2 Cash Flow
PV2=1.10260,000 PV2=49,587
Step 3: Calculate Total Present Value
Total PV=54,545+49,587 Total PV=1,04,132
Step 4: Calculate NPV
NPV=1,04,132−1,00,000 NPV=₹4,132
👉 Since NPV is positive, the project is financially acceptable.
7️⃣ Example 2: Urban Parking Facility
Initial Investment = ₹2,50,00,000
Annual Net Cash Flow = ₹40,00,000
Project Life = 5 years
Discount Rate = 12%
Using discount formula:
Year 1:
40,00,000/1.12=35,71,429
Year 2:
40,00,000/1.122=31,88,776
Year 3:
40,00,000/1.123=28,47,120
Year 4:
40,00,000/1.124=25,41,179
Year 5:
40,00,000/1.125=22,69,803
Total Present Value of Benefits:
≈ ₹1,44,18,307
NPV Calculation:
NPV=1,44,18,307−2,50,00,000 NPV=−₹1,05,81,693
👉 Negative NPV → Project not viable at 12% discount rate.
8️⃣ Applications in Planning
🔹 1. Transit-Oriented Development (TOD)
Used to assess:
- Increased land value
- Rental growth near transit
- Long-term commercial viability
🔹 2. Infrastructure Projects
- Metro rail
- Bus terminals
- Multi-modal hubs
- Flyovers
🔹 3. Sustainable Building Projects
- Solar energy systems
- Green roofing
- Energy-efficient retrofitting
🔹 4. Public-Private Partnership (PPP)
NPV helps determine:
- Financial feasibility
- Concession duration
- Revenue sharing models
9️⃣ Advantages of NPV
✔ Considers time value of money
✔ Measures absolute profit
✔ Suitable for long-term projects
✔ Reliable for infrastructure evaluation
✔ Widely accepted in financial analysis
🔟 Limitations
❌ Requires selection of discount rate
❌ Complex compared to ROI
❌ Sensitive to future cash flow estimation
❌ Hard to monetize social benefits
11️⃣ Difference Between ROI and NPV
| ROI | NPV |
|---|---|
| Percentage measure | Absolute monetary value |
| Ignores time value | Considers time value |
| Simple | More accurate |
| Short-term focus | Long-term focus |
12️⃣ Conclusion
Net Present Value (NPV) is one of the most important financial tools in architecture and urban planning. It allows planners and architects to:
- Evaluate long-term project feasibility
- Compare alternative design options
- Assess infrastructure viability
- Support sustainable development decisions
- Strengthen Detailed Project Reports (DPRs)
NPV ensures that planning decisions are economically sound, financially sustainable, and aligned with long-term urban growth strategies.
