
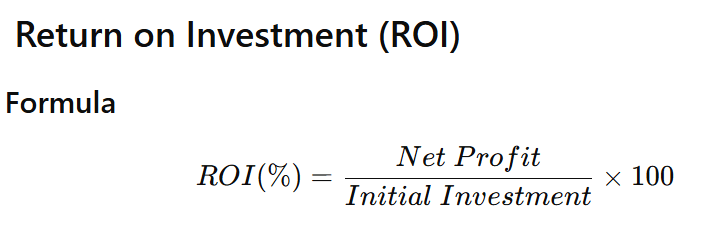
Return on Investment (ROI) in Architecture and Planning Projects
1️⃣ What is Return on Investment (ROI)?
Return on Investment (ROI) is a financial performance indicator used to evaluate the profitability of an investment. It measures how much return is generated relative to the cost invested in a project.
🔹 Formula
ROI(%)=Initial InvestmentNet Profit×100
Where:Net Profit=Total Gain−Initial Investment
ROI expresses profitability as a percentage, making it easy to compare different projects.
2️⃣ Why ROI is Important in Architecture and Planning
In architecture and urban planning projects, investments are usually large and long-term. ROI helps:
- Assess financial feasibility
- Compare alternative design options
- Justify project approval to stakeholders
- Evaluate redevelopment projects
- Support public-private partnership (PPP) decisions
- Prioritize infrastructure investments
For planners and architects, ROI bridges design thinking and economic rationality.
3️⃣ Where ROI is Used in Architecture and Planning
1. Real Estate Development Projects
- Residential apartments
- Commercial office buildings
- Shopping malls
- Mixed-use developments
2. Urban Redevelopment Projects
- Brownfield redevelopment
- Transit-Oriented Development (TOD) zones
- Heritage adaptive reuse
3. Infrastructure Projects
- Parking structures
- Bus terminals
- Metro station area development
- Smart city projects
4. Sustainable Design Decisions
- Solar panel installation
- Rainwater harvesting systems
- Energy-efficient façades
- Green building materials
5. Public Projects (Cost-Benefit Support)
- Urban parks
- Pedestrian infrastructure
- Streetscape improvements
4️⃣ How to Use ROI in Architecture and Planning Projects
Step 1: Identify Initial Investment
Include:
- Land cost
- Construction cost
- Consultant fees
- Approval charges
- Equipment cost
- Marketing cost
Step 2: Estimate Total Return
Returns may include:
- Sale revenue
- Rental income
- Increased property value
- Energy savings
- Reduced maintenance cost
- Increased tax revenue (public projects)
Step 3: Calculate Net Profit
Net Profit=Total Returns−Initial Investment
Step 4: Apply ROI Formula
ROI=Initial InvestmentNet Profit×100
5️⃣ Detailed Examples in Architecture & Planning Context
✅ Example 1: Residential Apartment Project
Initial Investment:
- Land: ₹40,00,000
- Construction: ₹50,00,000
- Other costs: ₹10,00,000
Total Investment = ₹1,00,00,000
Total Sales Revenue = ₹1,25,00,000
Net Profit:1,25,00,000−1,00,00,000=25,00,000 ROI=1,00,00,00025,00,000×100 ROI=25%
👉 This indicates strong financial viability.
✅ Example 2: Solar Panel Installation in Commercial Building
Installation Cost = ₹5,00,000
Annual Energy Savings = ₹80,000
Project Life Considered = 5 years
Total Savings in 5 years:80,000×5=4,00,000
Assume property value increase = ₹2,20,000
Total Return = ₹6,20,000
Net Profit:6,20,000−5,00,000=1,20,000 ROI=5,00,0001,20,000×100 ROI=24%
👉 Supports sustainable investment decision.
✅ Example 3: Parking Structure in Urban Area
Investment = ₹2,50,00,000
Total Parking Revenue over 5 years = ₹2,75,00,000
Net Profit:2,75,00,000−2,50,00,000=25,00,000 ROI=2,50,00,00025,00,000×100 ROI=10%
👉 Moderate ROI; planner may compare alternatives.
6️⃣ ROI in Urban Planning Decision-Making
ROI helps in:
✔ Comparing Design Alternatives
Example:
- Glass façade vs energy-efficient façade
- Conventional materials vs green materials
✔ Evaluating TOD Projects
- Increased land value near transit
- Higher rental income
- Increased density returns
✔ Public Investment Justification
- Economic multiplier effects
- Tax increment financing
- Urban regeneration impact
7️⃣ Advantages of ROI in Planning
- Simple to calculate
- Easy to interpret
- Comparable across projects
- Useful for private investors
- Supports financial feasibility studies
8️⃣ Limitations of ROI in Architecture & Planning
- Does not consider time value of money
- Ignores social and environmental benefits
- Not suitable alone for long-term public projects
- Does not capture intangible value (livability, safety, aesthetics)
Therefore, ROI should be used along with:
- Net Present Value (NPV)
- Internal Rate of Return (IRR)
- Cost-Benefit Analysis (CBA)
- Social Return on Investment (SROI)
9️⃣ Practical Application for Architects & Planners
When preparing a Detailed Project Report (DPR):
- Estimate project cost
- Forecast revenue or savings
- Compute ROI
- Compare multiple scenarios
- Present ROI to clients/investors
- Use ROI to optimize design choices
🔟 Conclusion
Return on Investment (ROI) is a fundamental financial tool that connects design, planning, and economics. In architecture and urban planning, ROI supports:
- Investment decisions
- Sustainable design adoption
- Real estate feasibility
- Infrastructure planning
- Policy justification
While ROI is not sufficient alone for public welfare projects, it remains essential for financially driven development and strategic planning decisions.

You must be logged in to post a comment.