– Shashikant Nishant Sharma
Enhancing safety analysis at uncontrolled traffic intersections is a critical endeavor, and surrogate methods provide a transformative approach to achieve this goal. Uncontrolled traffic intersections, lacking conventional traffic control mechanisms, often present heightened safety risks. Surrogate safety analysis methods offer an innovative way to overcome the challenges posed by the absence of historical crash data. By utilizing surrogate measures like vehicle trajectories, speeds, and accelerations, these methods allow for a proactive assessment of potential safety risks. Instead of relying solely on past accident records, surrogate safety analysis leverages real-time or simulated data to predict conflict points and hazardous events, enabling timely and targeted safety interventions. This forward-looking methodology holds immense promise in improving safety outcomes at uncontrolled intersections, ultimately contributing to a safer and more efficient road network.
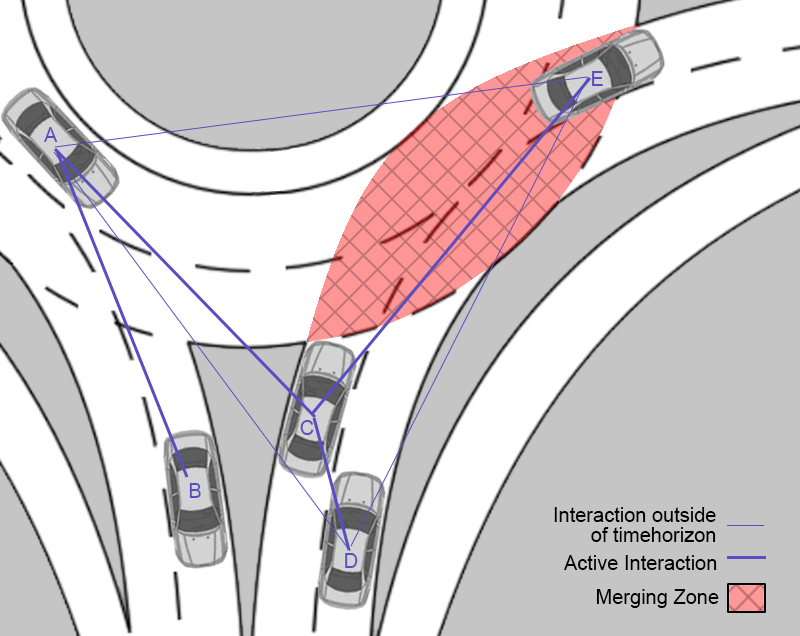
Uncontrolled traffic intersections pose a significant challenge for traffic engineers and planners in ensuring safety for road users. These intersections, lacking traffic signals or stop signs, require advanced analytical approaches to comprehend and mitigate potential safety risks effectively. One such promising approach is the use of surrogate safety analysis methods, which offer a proactive means to identify potential safety concerns and implement appropriate countermeasures.
Understanding the Challenge
Uncontrolled traffic intersections, often found in suburban or rural areas, demand a careful examination of vehicle interactions to predict and mitigate potential collisions. The absence of traffic control devices necessitates a thorough analysis of driver behavior, traffic flow patterns, and geometric design to assess safety implications accurately.
Traditional safety analyses rely heavily on historical crash data, making it challenging to predict and prevent accidents in areas with minimal crash records. Surrogate safety analysis methods address this limitation by utilizing real-time or simulated traffic data to predict potential safety issues and recommend appropriate safety enhancements.
The Surrogate Safety Analysis Method
The surrogate safety analysis method involves utilizing surrogate measures, such as vehicle trajectories, speeds, accelerations, and lane positions, to estimate the likelihood of safety-critical events. These surrogate measures act as proxies for actual safety outcomes, providing insights into potential conflicts or risky situations without relying on historical crash data.
Key Components and Techniques
- Conflict Analysis: Surrogate safety analysis focuses on identifying conflicts or near-miss events, providing crucial insights into potentially hazardous scenarios. By analyzing vehicle trajectories and behaviors, engineers can pinpoint locations and patterns where conflicts are likely to occur.
- Microscopic Simulation: Utilizing microsimulation models allows for the generation of a virtual representation of traffic behavior at uncontrolled intersections. This enables a comprehensive analysis of various parameters, such as traffic density, vehicle speed, and maneuvering patterns, aiding in predicting potential conflict points.
- Safety Performance Indicators (SPIs): SPIs are quantitative measures derived from surrogate measures that provide a structured approach to assess safety. Common SPIs include time to collision (TTC), post-encroachment time (PET), and speed profiles. Analyzing these indicators helps in identifying critical areas and evaluating the effectiveness of safety interventions.
Advantages of Surrogate Safety Analysis
- Proactive Safety Assessment: Surrogate methods enable a proactive safety assessment by predicting potential safety concerns before accidents occur, allowing for timely interventions and proactive planning. Surrogate methods play a pivotal role in enabling a proactive safety assessment of intersections. By utilizing surrogate measures like Time-to-Collision (TTC) and Post-Encroachment Time (PET), potential safety concerns can be predicted before actual accidents occur. This predictive capability allows traffic engineers and safety experts to take timely interventions and plan proactive measures to mitigate identified risks. This proactive approach significantly contributes to improving overall traffic safety by addressing issues before they escalate into serious accidents.
- Cost-Effective Analysis: Unlike traditional safety analyses that heavily rely on crash data collection and analysis, surrogate methods are cost-effective as they leverage readily available real-time or simulated data. Surrogate safety analysis presents a cost-effective alternative to traditional safety analyses that heavily rely on crash data collection and analysis. The reliance on readily available real-time or simulated data means that there is no need for extensive and expensive crash data collection efforts. This translates to cost savings in terms of data acquisition, processing, and analysis. Moreover, the efficient utilization of existing data sources enhances the overall cost-effectiveness of implementing safety improvements at intersections.
- Enhanced Decision-Making: By providing a deeper understanding of conflict points and risk factors, surrogate safety analysis supports informed decision-making for implementing targeted safety improvements. Surrogate safety analysis provides a deeper and more nuanced understanding of conflict points, risk factors, and potential safety hazards at an intersection. This enhanced understanding empowers decision-makers, including traffic engineers, urban planners, and policymakers, to make well-informed and evidence-based decisions regarding safety improvements. By identifying critical areas and conflicts, decision-makers can strategically allocate resources and implement targeted countermeasures, such as geometric improvements, traffic signal optimizations, or signage enhancements. Informed decision-making based on surrogate safety analysis helps optimize safety interventions and maximize their effectiveness in reducing accidents and improving overall traffic safety.
Implementing Surrogate Safety Analysis for Uncontrolled Intersections
- Data Collection and Analysis: Gather real-time or simulated traffic data, including vehicle trajectories, speeds, and lane positions. Analyze this data to identify patterns and potential conflict points. To comprehensively understand traffic dynamics at an intersection, a thorough data collection process is essential. Real-time or simulated traffic data should be gathered, encompassing various parameters like vehicle trajectories, speeds, and lane positions. This data can be obtained through advanced traffic monitoring systems, such as video cameras, sensors embedded in the road, or connected vehicle technologies. The collected data is then subjected to rigorous analysis using statistical and data analytics techniques to identify patterns, trends, and potential conflict points within the intersection.
- Surrogate Measure Identification: Choose appropriate surrogate measures (e.g., TTC, PET) relevant to the intersection type and traffic conditions to estimate safety performance. In order to gauge the safety performance at the intersection, appropriate surrogate measures need to be identified. Surrogate measures serve as proxies for actual safety outcomes and are crucial for evaluating the safety of a given intersection under different traffic conditions. Common surrogate measures include Time-to-Collision (TTC), Post-Encroachment Time (PET), and others that are relevant to the intersection type and the prevailing traffic conditions. These measures provide valuable insights into potential conflicts and near-miss events.
- Conflict Identification and Countermeasures: Utilize surrogate measures to identify conflicts and critical areas within the intersection. Implement appropriate countermeasures such as geometric improvements, signage enhancements, or traffic calming measures. Leveraging the identified surrogate measures, conflicts and critical areas within the intersection can be pinpointed. Conflicts are instances where the surrogate measures suggest a heightened risk of a collision or unsafe traffic interactions. Through a thorough analysis of these conflicts, specific critical areas within the intersection can be identified. To enhance safety and mitigate conflicts, appropriate countermeasures should be implemented. These countermeasures could encompass a range of strategies, including geometric improvements to the intersection layout, optimizing lane configurations, enhancing visibility through improved signage and lighting, employing traffic calming measures such as speed bumps or roundabouts, or implementing intelligent traffic signal control systems. These interventions aim to create a safer environment by reducing conflict points and minimizing the risk of accidents. Ultimately, this holistic approach involving data collection, surrogate measure identification, and conflict analysis coupled with targeted countermeasures is essential for enhancing intersection safety and optimizing traffic flow. Ongoing monitoring and evaluation of these measures are crucial to ensure sustained safety improvements at the intersection.
Conclusion
The adoption of surrogate safety analysis methods represents a significant leap forward in improving safety at uncontrolled traffic intersections. By relying on real-time or simulated data, traffic engineers can predict potential conflicts and hazardous scenarios, enabling the implementation of proactive safety measures. Embracing this approach is crucial for achieving a safer and more efficient transportation network, ultimately saving lives and reducing the overall societal cost of traffic accidents. In summary, surrogate safety analysis offers a proactive and cost-effective approach to evaluating and enhancing traffic safety at intersections. It enables the prediction of safety concerns, optimizes resource allocation, and supports well-informed decision-making, all of which are critical aspects for creating safer road environments and reducing the likelihood and severity of accidents.
References
Mohamed, M. G., & Saunier, N. (2013). Motion prediction methods for surrogate safety analysis. Transportation research record, 2386(1), 168-178.
Sharma, S. N. (2019). Review of most used urban growth models. In International Journal of Advanced Research in Engineering and Technology (IJARET) (Vol. 10, Issue 3, pp. 397–405). Zenodo. https://doi.org/10.5281/ZENODO.8169002
Sharma, S. N., & Singh, D. (2023). Understanding mid-block traffic analysis: A crucial tool for road safety. Think India Journal, 26(3), 5–9. https://www.thinkindiaquarterly.org/index.php/think-india/article/view/20406
Singh, D., & Das, P. (2023). A review on surrogate safety measures in safety evaluation and analysis. In Proceedings of the Sixth International Conference of Transportation Research Group of India (pp. 113–129). Springer Nature Singapore.
Singh, D. (2023). Surrogate safety evaluation at uncontrolled intersection in non-Lane base traffic conditions. European Transport, 93, 1–16. https://doi.org/10.48295/et.2023.93.11

You must be logged in to post a comment.