What is OOPS ?
It is a programming paradigm based on a concept of objects and classes. It allows the programmer to work with real life entities like inheritance, polymorphism, hiding, etc. Some popular object-oriented programming languages are Java, C++, Python, PHP, etc.
Before diving into the concept of OOPS, you should be familiar with object and classes.
Object – These are the real world entities having a specific identity, specific characteristics and behavior you find in your everyday life.
Classes – It is the blueprint that represents a set of objects that share common characteristics and behavior.
‘Object’ is an instance of ‘class’. For example, ‘bird’ is a class but ‘eagle’ is an object.

The four pillars of object-oriented programming are –
- Abstraction
- Encapsulation
- Inheritance
- Polymorphism
Let’s take a look at these concepts –
Abstraction
It is the method of hiding the implementation details and showing only the functionality to the user.
For example, when we are driving a car to the grocery store ignoring the details of how the engine, braking systems works. We think car as an object with its own unique behavior. We are only interested in how to propel the car forward and reach the destination. The user need not be concerned about how a particular feature is implemented. From the outside, the car is a single entity. But from inside, you see that the car consists of several systems – brakes, sound system, steering wheel, and so on.
Encapsulation
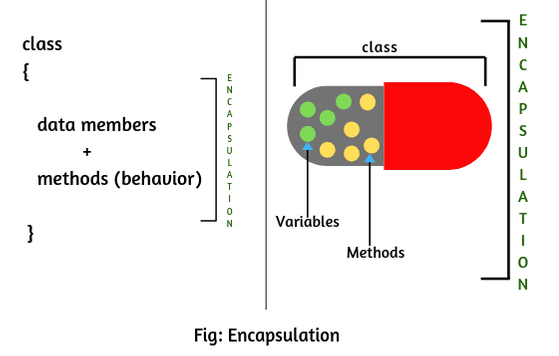
It is an object-oriented programming concept that binds together the data and functions that manipulate the data and keeps both safe from outside interference. In other words, encapsulation is a programming technique that binds the class members (variables and methods) together and prevents them from being accessed by other classes. Therefore, it is also called data mining.
For example, a capsule encapsulates several ingredients of the medicine. The mixture of medicines are variables and methods then the capsule will act as a class and the whole process is called encapsulation as shown in the figure given below.
Inheritance
Inheritance is the process by which one object acquires the properties of another object. It is important because it supports the concept of hierarchical classification.
For example, the Cat extends the Mammal class, which extends the Animal class. So cat would directly inherit all the functions from Animal and Mammal class.
It represents an IS-A type of relationship. From the above example, we can say that cat is a mammal, which is a mammal. So anything that applied to animals also applies to a cat. This will make more sense when you will be writing complicated code and using inheritance for the reusability of code.
Polymorphism
Polymorphism (from Greek, meaning “many forms”) is a feature that allows one interface to be used for a general class of action. A specific action is determined by the exact nature of the situation. In simple words, it means one function behaves in different forms.
For example, a dog’s sense of smell is polymorphic. If a dog smells cat, it will bark and run after it, if the dog smells its food, it salivates and run to its bowl.
Reference Link : https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Object-oriented_programming
