By Shashikant Nishant Sharma
The University Grants Commission (UGC), one of the statutory organizations, is a key player in maintaining the quality of education across Indian institutions.
Right from evaluating teaching-learning practices to bringing innovations in the field of education, UGC introduces various schemes from time to time for quality assurance.
Continuing the chain of building transformative educational setup, UGC has introduced the “Academic Bank of Credits” (ABC). It helps faculty to manage & check the credits earned by students.
Before we get into details, let us understand the main objectives of ABC…
- To promote student-centric education
- Focus on learner-friendly teaching approaches
- Implement an inter-disciplinary approach
- Allow students to learn the best courses of their interest
- Enable students to learn at their own pace
Keeping these objectives in mind, Prime Minister Narendra Modi introduced the National Education Policy (NEP 2020) and the Academic Bank of Credits is a vital part of the policy.
What is the Academic Bank of Credits (ABC)?
Academic Bank of Credits (ABC) is a virtual/digital storehouse that contains the information of the credits earned by individual students throughout their learning journey. It will enable students to open their accounts and give multiple options for entering and leaving colleges or universities. There will be “multiple exits” & “multiple entries” points during the higher education tenure & credits will be transferred through the ABC seamlessly.
ABC can be considered as an authentic reference to check the credit record of any student at any given point in time. Thus, the concept of ABC is fuel to boost the efficiency of faculty and help students embrace a multi-disciplinary educational approach. The idea is to make students “skillful professionals” and help their overall growth.
In a crux, the Academic Bank of Credits will be a game-changer in transforming Indian education to a great extent.
Functions of Academic Bank of Credit (ABC)
- The Academic Bank will be accountable for opening, closing, and validating the academic accounts of students.
- It will carry out tasks such as credit accumulation, credit verification, credit transfer/redemption of students.
- The courses include online and distance mode courses offered by the government and institutes.
- The validity of these academic credits earned by students will be up to seven years and students can redeem these credits.
- The credits can be redeemed and students can seek admission directly in the second year at any university.
- The validity will be up to seven years, hence, students will have to rejoin within seven years.
Importance of Academic Bank of Credit (ABC)
- Increases the student’s freedom in choosing their courses and academics.
- Enables the student to drop out in any year and then exchange the credits earned so far with a certificate/diploma if they are eligible.
- They can redeem the credits and rejoin the same or any other institute in the future and continue their education.
- The institutes cannot keep the students in the courses against their will to earn money
How does the Academic Bank of Credits Work?
As I mentioned to you earlier, the Academic Bank of Credits (ABC) would act as a reference point for faculty to check the credit records of students. The students need to follow the given guidelines to be a part of the ABC.
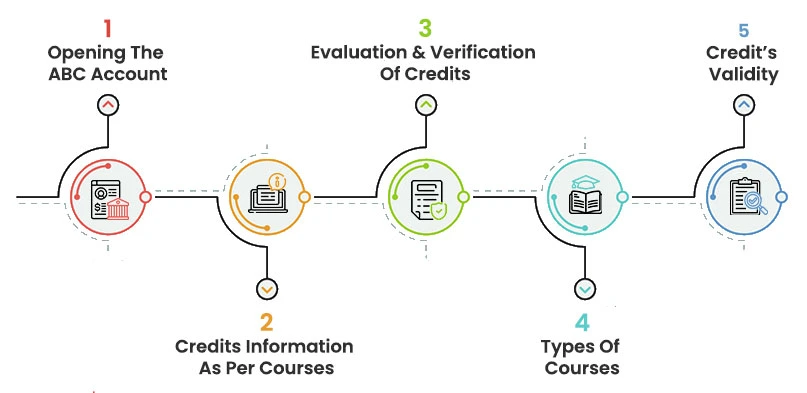
#1: Opening The ABC Account
First and foremost, the students need to open an Academic Bank Account.
They might require details like their name, address, certificates, course details, etc to create the ABC account.
A unique ID & password will be created from where students can log in at any given point to check their earned credits.
#2: Credits Information As Per Courses
As per the courses, a credit structure will be created by the Government.
When a student pursues any course and clears exams, credits will be automatically awarded to them. Institutions need to fill out the details and upload the deposits in the students’ Academic Credit Bank’s account on the digital portal.
#3: Evaluation & Verification Of Credits
Any kind of credit evaluation & verification will be carried out by the Academic Credit Bank at regular intervals.
If students want to transfer the credits, they need to approach the ABC for further process.
It will help in regulating the processes with ultimate authenticity.
#4: Types Of Courses
Online & offline – both types of courses are included in the scheme. Some of the important ones include National Schemes such as–
- NPTEL
- SWAYAM
- V-LAB
Thus, the ABC will cover almost all types of courses including distance learning courses to help students of every possible stream.
#5: Credit’s Validity
The credits earned by students will be valid for seven years.
However, the validity of credits is subject to change depending on the type of courses or disciplines.
In such instances, ABC will provide the details of the exceptions to students.
Even if a student takes a break or is not able to continue their education, they may redeem the earned credits in the future within the time limit of seven years.
Expected Impact of ABC on Educational System
The UGC expects a positive impact that will be brought via the practice of the ABC in the upcoming years. HEIs who participate in the scheme will be highly benefited due to the smooth management of credits.
The inter-disciplinary & multi-disciplinary approach is the need of the hour. With the Academic Credit Bank, HEIs will be able to help students learn subjects of their choice and become “skill-oriented” graduates.
For further details, you may visit the ABC’s official website.
References
Gawas, N. M., Naik, G. R., & Kapdi, G. Academic Bank of Credits (ABC): A Big Fish in a Big Pond. Anand Bihari, 152.
Mandale, K., & Killedar, S. (2023). Benefits of the Academic Bank of Credits ABC According to New Education Policy NEP 2020. PRARUP PUBLICATION A/p. Hatkanangale, Tal. Hatkanangale Dist. Kolhapur-416 004 (Maharashtra), 23-28.
Naveen, H. M. (2021). Establishment and Operation of Academic Bank of Credits (ABC) in Higher Education. International Journal of Engineering Applied Science and Technology, 6(5), 166-169.
Sharma, S. N., & Dehalwar, K. (2023). Council of Planning for Promoting Planning Education and Planning Professionals. Journal of Planning Education and Research, 43(4), 748-749.
Vashistha, N., Dhiman, A., Grima, S., & Kiran, S. (2022). National academic credit bank: Need of times. In Edutech enabled teaching (pp. 201-216). Chapman and Hall/CRC.
